|

Dictionary
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
- indefinitely
- An unspecified amount, having no exact limits (cf Infinity and Iteration Discussion).
- independent events
- Two events A and B are independent if the probability that they happen at the same
time is the product of the probabilities that each occurs individually; i.e., if
P(A & B) = P(A)P(B). In other words, learning that one event occurs does not give any
information about whether the other event occurred too: the conditional probability
of A given B is the same as the unconditional probability of A, i.e., P(A/B) = P(A).
- infinity
- Greater than any fixed counting number, or extending forever. No matter how large a number one thinks of, infinity is larger than it. Infinity has no limits
(cf Infinity and Iteration Discussion).
- initiator
- A line-segment or figure that begins as the beginning geometric shape for a fractal. The initiator is then replaced by the generator for the fractal.
- input
- The number or value that is entered, for example, into a function machine. The
number that goes into the machine is the input (cf Functions as Processes or Rules Discussion).
- integer
- Any positive or negative number that does not include a fraction or decimal, including zero.
- intersection of sets
- The intersection of two or more sets is the set of elements that all the sets have
in common; in other words, all the elements contained in every one of the sets. The
mathematical symbol for intersection is
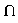 (cf Internet Search and Set Operations Discussion).
(cf Internet Search and Set Operations Discussion).
- intercept
- See x-intercept or y-intercept
(cfLinear Functions
Discussion).
- irregular fractals
- Complex fractals whose dimension is often difficult to determine and in some cases is unknown (cf Dimension for Irregular Fractals Discussion).
- isosceles triangle
- A
triangle that has at least two congruent sides (cfTrapezoid Discussion).
- item
- The things or objects that are the subject of a bar graph (cf Class Interval: Scale and Impression Discussion).
- iteration
- Repeating a set of rules
or steps over and over. One step is called an iterate.
(cf Infinity and Iteration Discussion).
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
R
S
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Z
|