

GEOTHERMAL ENERGY
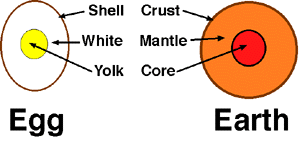 Have you ever cut a boiled egg in half without peeling the shell? The egg
is what the earth looks like inside. The yellow yolk of the egg is like the
core of the earth. The white part is the mantle of the earth. And the thin
shell of the egg is like the earth's crust.
Have you ever cut a boiled egg in half without peeling the shell? The egg
is what the earth looks like inside. The yellow yolk of the egg is like the
core of the earth. The white part is the mantle of the earth. And the thin
shell of the egg is like the earth's crust.
Below the crust of the earth, the top layer of the mantle is hot, liquid rock called magma. The crust of the earth floats on this liquid magma mantle. When magma breaks through the surface of the earth in a volcano, it is called lava.
 For every 100 meters
you go below ground, the temperature of the rock increases
about 3 degrees Celsius. Or for every 328 feet below ground, the temperature
increases 5.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
For every 100 meters
you go below ground, the temperature of the rock increases
about 3 degrees Celsius. Or for every 328 feet below ground, the temperature
increases 5.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
Deep under the surface, water sometimes makes its way close to the hot rock and turns into hot water or into steam. The hot water can reach temperatures of more than 300 degrees Fahrenheit or 148 degrees Celsius. This is hotter than boiling water.
When this hot water comes up through a crack
in the earth, we call it a geyser or hot spring like the one to the right.
Sometimes people use the hot water in swimming pools or in health spas.
 The hot water from below the ground can warm buildings, like the green house
on the right, for growing plants.
The hot water from below the ground can warm buildings, like the green house
on the right, for growing plants.
In some places, like in San Bernardino in Southern California, hot water from below ground is used to heat buildings during the winter. The hot water runs through miles of insulated pipes to dozens of public buildings. The City Hall, animal shelters, retirement homes, state agencies, a hotel and convention center are some of the buildings which are heated this way.
In Iceland, many of the buildings and even
swimming pools in the capital of Reykjavik and elsewhere are heated with geothermal
hot water. The country has at least 25 active volcanoes, and many hot springs
and geysers.
FOSSIL FUELS - COAL, OIL, AND NATURAL
GAS
 There are three major forms of fossil fuels: coal, oil and natural gas. All
three were formed many hundreds millions of years ago before the time of the
dinosaurs -- hence the name fossil fuels. The age they were formed is called
the Carboniferous period, getting its name from carbon the basic element in
coal and other fossil fuels.
There are three major forms of fossil fuels: coal, oil and natural gas. All
three were formed many hundreds millions of years ago before the time of the
dinosaurs -- hence the name fossil fuels. The age they were formed is called
the Carboniferous period, getting its name from carbon the basic element in
coal and other fossil fuels.
Fossil fuels are made up of decomposed plant and animal matter. Plants change energy they receive from the sun into stored energy. This energy is food used by the plant. This is called photosynthesis. Animals eat plants to make energy. And people eat animals and plants to get energy to do work.
When plants and other ancient creatures died, they decomposed and became buried, layer upon layer under the ground. It took millions of years to form these layers into a hard, black colored rock-like substance called coal, a thick liquid called oil or petroleum, and natural gas. Fossil fuels can be found under the earth in many locations around the country.
Each of the fossil fuels is extracted out of the ground differently.
 To find oil and natural gas, companies drill through the earth to the deposits
deep below the surface. The oil and natural gas are then pumped from below the
ground by oil rigs (like in the picture above). They then usually travel through
pipelines, like the ones in the picture to the right in Alaska.
The petroleum or crude oil must be changed or refined into other products before
it can be used.
To find oil and natural gas, companies drill through the earth to the deposits
deep below the surface. The oil and natural gas are then pumped from below the
ground by oil rigs (like in the picture above). They then usually travel through
pipelines, like the ones in the picture to the right in Alaska.
The petroleum or crude oil must be changed or refined into other products before
it can be used.
 Oil is stored in large tanks until it is sent to various places to be used.
Oil is stored in large tanks until it is sent to various places to be used.
Oil is also made into many different products -- fertilizers for farms, the clothes you wear, the toothbrush you use, the plastic bottle that holds your milk, the plastic pen that you write with. They all came from oil.
There are thousands of other products that come from oil. Almost all plastic comes originally from oil. Can you think of some things made from oil?
At oil refineries, crude oil is split into various types of products by heating the thick black oil.
The products include gasoline, diesel fuel, aviation fuel, home heating oil, oil for ships and oil to burn in power plants to make electricity.
 Natural
gas is lighter than air. Natural gas is mostly made up of a gas called methane.
Methane is a simple chemical compound that is made up of carbon and hydrogen
atoms. It's chemical formula is CH4. This gas is highly flammable.
Natural
gas is lighter than air. Natural gas is mostly made up of a gas called methane.
Methane is a simple chemical compound that is made up of carbon and hydrogen
atoms. It's chemical formula is CH4. This gas is highly flammable.
Natural gas is usually found near petroleum underground. The natural gas is pumped from below ground and sent in large pipelines like the ones to the right.
Natural gas usually has no odor and you can't see it. Before it is sent to the pipelines and storage tanks, it is mixed with a chemical that gives a strong odor. The odor smells almost like rotten eggs. The odor makes it easy to smell if there is a leak.
From the storage tanks natural gas is sent through underground pipes to your home to cook your food and heat your house. Natural gas is also sent to factories and to power plants to make electricity.
So, it's best to not waste fossil fuels. They are not renewable; they can't really be made again.
We can save fossil fuels by conserving energy.
HYDRO POWER
 When it rains in hills and mountains, the water becomes streams and rivers
that run down to the ocean. The moving or falling water can be used to do
work. Energy, you'll remember is the ability to do work. So moving water,
which has kinetic energy, can be used as a source of energy.
When it rains in hills and mountains, the water becomes streams and rivers
that run down to the ocean. The moving or falling water can be used to do
work. Energy, you'll remember is the ability to do work. So moving water,
which has kinetic energy, can be used as a source of energy.
For hundreds of years, moving water was used to turn wooden wheels that were attached to grinding wheels to grind flour or corn. Today, moving water can also be used to make electricity.
Hydro means water. Hydro-electric means making electricity from water power.
Hydroelectric power uses the kinetic energy of moving water to make electricity. Dams can be built to stop the flow of a river. Water behind a dam often forms a reservoir. Dams are also built across larger rivers but no reservoir is made. The river is simply sent through a hydroelectric power plant.
The water flows through a pipe called a penstock and pushes against blades in a turbine, causing them to turn. The turbine spins a generator to produce electricity. The electricity can then go to your home, to your school, to factories and businesses.
NUCLEAR ENERGY - Fission
and Fusion
Another major form of energy is nuclear energy, the energy that is trapped
inside each atom. One of the laws of the universe is that matter and energy
can't be created nor destroyed. But they can be changed in form.
Matter can be changed into energy. The famous scientist Albert Einstein created the mathematical formula that explains this. It is:
E [energy] equals m [mass] times c2 [c stands for the speed of light. c2 means c times c, or the speed of light raised to the second power -- or c-squared.]
Please note that some web browser software may not show an exponent (raising something to a power, a mathematical expression) on the Internet. Normally c-squared is shown with a smaller "2" placed above and to the right of the c.
 Scientists used Einstein's famous equation as the key to unlock atomic energy
and also create atomic bombs.
Scientists used Einstein's famous equation as the key to unlock atomic energy
and also create atomic bombs.
The ancient Greeks said the smallest part of nature is an atom. But they did not know 2,000 years ago about nature's even smaller parts.
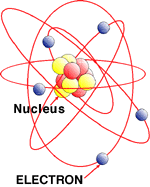
As we learned in the "What is Electricity?" section, atoms are made up of smaller particles -- a nucleus of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons which swirl around the nucleus much like the earth revolves around the sun.
 A nuclear power plant (like Diablo Canyon Nuclear Plant shown on the right)
uses uranium as a "fuel". Uranium is an element that is dug out of the ground
many places around the world. It is processed into tiny pellets that are loaded
into very long rods that are put into the power plant's reactor.
A nuclear power plant (like Diablo Canyon Nuclear Plant shown on the right)
uses uranium as a "fuel". Uranium is an element that is dug out of the ground
many places around the world. It is processed into tiny pellets that are loaded
into very long rods that are put into the power plant's reactor.
Inside the reactor of an atomic power plant, uranium atoms are split apart in a controlled chain reaction.
In a chain reaction, particles released by the splitting of the atom go off and strike other uranium atoms splitting those. Those particles given off split still other atoms in a chain reaction. In nuclear power plants, control rods are used to keep the splitting regulated so it doesn't go too fast.
If the reaction is not controlled, you could have an atomic bomb. But in atomic bombs, almost pure pieces of the element Uranium-235 or Plutonium, of a precise mass and shape, must be brought together and held together, with great force. These conditions are not present in a nuclear reactor.
The reaction also creates radioactive material. This material could hurt people if released, so it is kept in a solid form. The very strong concrete dome in the picture is designed to keep this material inside if an accident happens.
This chain reaction gives off heat energy. This heat energy is used to boil water in the core of the reactor. So, instead of burning a fuel, nuclear power plants use the chain reaction of atoms splitting to change the energy of atoms into heat energy.
This water from around the nuclear core is sent to another section of the power plant. Here it heats another set of pipes filled with water to make steam. The steam in this second set of pipes powers a turbine to generate electricity.
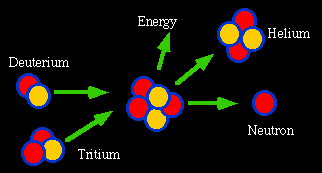 Another
form of nuclear energy is called fusion. Fusion means joining smaller nuclei
(the plural of nucleus) to make a larger nucleus. The sun uses nuclear fusion
of hydrogen atoms into helium atoms. This gives off heat and light and other
radiation.
Another
form of nuclear energy is called fusion. Fusion means joining smaller nuclei
(the plural of nucleus) to make a larger nucleus. The sun uses nuclear fusion
of hydrogen atoms into helium atoms. This gives off heat and light and other
radiation.
In the picture to the right, two types of hydrogen atoms, deuterium and tritium, combine to make a helium atom and an extra particle called a neutron.
Also given off in this fusion reaction is energy!
Scientists have been working on controlling nuclear fusion for a long time, trying to make a fusion reactor to produce electricity. But they have been having trouble learning how to control the reaction in a contained space.
What's better about nuclear fusion is that
it creates less radioactive material than fission, and its supply of fuel
can last longer than the sun.
OCEAN ENERGY
The world's ocean may eventually provide us with energy to power our homes
and businesses. Right now, most ocean energy power plants are only experimental
and are fairly small. But how can we get energy from the ocean?
There are three basic ways to tap the ocean for its energy. We can use the ocean's waves, we can use the ocean's high and low tides, or we can use temperature differences in the water. Let's take a look at each.
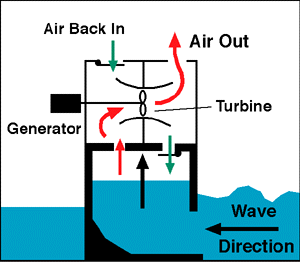 Kinetic energy (movement) exists in the moving waves of the ocean. That energy
can be used to power a turbine. In this simple example, to the right, the wave
rises into a chamber. The rising water forces the air out of the chamber. The
moving air spins a turbine which can turn a generator.
Kinetic energy (movement) exists in the moving waves of the ocean. That energy
can be used to power a turbine. In this simple example, to the right, the wave
rises into a chamber. The rising water forces the air out of the chamber. The
moving air spins a turbine which can turn a generator.
When the wave goes down, air flows through the turbine and back into the chamber through doors that are normally closed.
This is only one type of wave-energy system. Others actually use the up and down motion of the wave to power a piston that moves up and down inside a cylinder. That piston can also turn a generator.
Most wave-energy systems are very small. But, they can be used to power a warning buoy or a small light house.
In order for this to work well, you need large increases in tides. An increase of at least 16 feet between low tide to high tide is needed. There are only a few places where this tide change occurs around the earth. Some power plants are already operating using this idea. One plant in France makes enough energy from tides to power 240,000 homes.
Power plants can be built that use this difference in temperature to make energy. A difference of at least 38 degrees Fahrenheit is needed between the warmer surface water and the colder deep ocean water.
Using this type of energy source is called Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion or OTEC. It is being used in both Japan and in Hawaii in some demonstration projects.
SOLAR ENERGY
 When we hang laundry outside to dry in the sun, we are using the sun's heat
to do work -- drying our clothes.
When we hang laundry outside to dry in the sun, we are using the sun's heat
to do work -- drying our clothes.
The sun has always been an energy source.
Plants use the sun's light to make food. Animals eat plants for food.
And as we found out earlier, decaying plants and animals millions of years ago produced the coal, oil and natural gas that we use today.
So, fossil fuels actually got their start as sunlight many millions of years ago.
The sun can also be used to heat water for hot water in our homes and businesses.
 Many homes used solar water heaters. In 1897, 30 percent of the homes in Pasadena,
just east of Los Angeles, were equipped with solar water heaters. As mechanical
improvements were made, solar systems were used in Arizona, Florida and many
other sunny parts of the United States.
Many homes used solar water heaters. In 1897, 30 percent of the homes in Pasadena,
just east of Los Angeles, were equipped with solar water heaters. As mechanical
improvements were made, solar systems were used in Arizona, Florida and many
other sunny parts of the United States.
By 1920, thousands of solar water heaters had been sold. But by then, large deposits of oil and natural gas were discovered in the western United States. As these low cost fuels became available, solar systems began to be replaced with heaters using fossil fuels.
Today, solar water heaters are making a come back. They heat water for use inside homes and businesses. They also heat swimming pools like in the picture.
Panels on the roof of a building, like the one above, contain water pipes. When the sun hits the panels and the pipes, the sunlight warms them.
That warmed water can then be used in a swimming pool.
 Solar can also be used to make electricity.
Solar can also be used to make electricity.
Some solar power plants, like the one in the picture to the right in California's Mojave Desert, use a highly curved mirror called a parabolic trough to focus the sunlight on a pipe running down a central point above the curve of the mirror. The mirror focusses the sunlight to strike the pipe, and it gets so hot that it can boil water into steam. That steam can then be used to turn a turbine to make electricity.
In California's Mojave desert, there are huge rows solar mirrors arranged in what's called "solar thermal power plants" that use this idea to make electricity for more than 350,000 homes. The problem with solar energy is that it works only when the sun is shining. So, on cloudy days and at night, the power plants can't create energy. Some solar plants, are a hybrid technology. During the daytime they use the sun. At night they use natural gas to boil the water so they can continue to make electricity.
 Another form of solar power plants to make electricity is called a Central
Tower Power Plant, like the one to the right.
Another form of solar power plants to make electricity is called a Central
Tower Power Plant, like the one to the right.
Sunlight is reflected off 1,800 mirrors circling the tall tower. The mirrors are called heliostats and turn to face the sun all day long.
The light is reflected back to the top of the tower in the center of the circle where a fluid is turned very hot by the sun's rays. That fluid can be used to boil water to make steam to turn a turbine and a generator.
This experimental power plant is called Solar II. It is being re-built in California's desert using newer technologies than when it was first built in the early 1980s. Solar II will use the sunlight to change heat into mechanical energy in the turbine.
The power plant will make enough electricity
to power about 10,000 homes. Scientists say larger central tower power plants
will be able to make electricity for 100,000 to 200,000 homes.
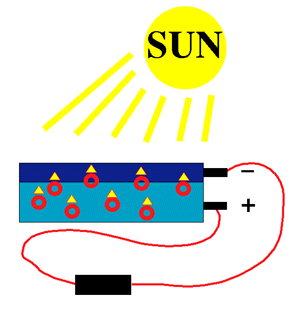 We can also change the sunlight directly to electricity using solar cells.
We can also change the sunlight directly to electricity using solar cells.
Solar cells are also called photovoltaic cells -- or PV cells for short -- and can be found on many small appliances, like calculators, and even on spacecraft. They were first developed in the 1950s for use on U.S. space satellites. They are made of silicon, a special type of melted sand.
When sunlight strikes the solar cell, electrons (red circles) are knocked loose. They move toward the treated front surface (dark blue color). An electron imbalance is created between the front and back. When the two surfaces are joined by a connector, like a wire, a current of electricity occurs between the negative and positive sides.
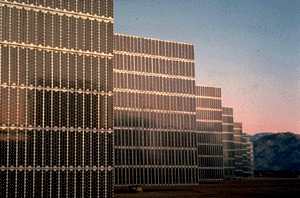 These
individual solar cells are arranged together in a PV module. Some of the modules
are set on special tracking devices to follow sunlight all day long.
These
individual solar cells are arranged together in a PV module. Some of the modules
are set on special tracking devices to follow sunlight all day long.
The electrical energy from solar cells can then be used directly. It can be used in a home for lights and appliances. It can be used in a business. Solar energy can be stored in batteries to light a roadside billboard at night. Or the energy can be stored in a battery for an emergency roadside cellular telephone when no telephone wires are around.
Some experimental cars also use PV cells. They convert sunlight directly into energy to power electric motors on the car.
WIND ENERGY
 Wind can be used to do work.
Wind can be used to do work.
The kinetic energy of the wind can be changed into other forms of energy, either mechanical energy or electrical energy.
When a boat lifts a sail, it is using wind energy to push it through the water. This is one form of work.
Farmers have been using wind energy for many years to pump water from wells using windmills like the one on the right.
In Holland, windmills have been used for centuries to pump water from low-lying areas.
Wind is also used to turn large grinding stones to grind wheat or corn, just like a water wheel is turned by water power.
Today, the wind is also used to make electricity.
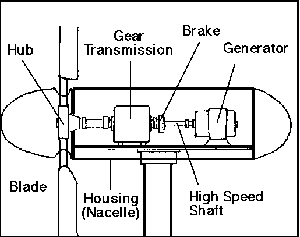 Blowing
wind spins the blades on a wind turbine -- just like a large toy pinwheel.
The blades are attached to a hub that is mounted on a turning shaft. The shaft
goes through a gear transmission box where the turning speed is increased.
The transmission is attached to a high speed shaft which turns a generator
that makes electricity.
Blowing
wind spins the blades on a wind turbine -- just like a large toy pinwheel.
The blades are attached to a hub that is mounted on a turning shaft. The shaft
goes through a gear transmission box where the turning speed is increased.
The transmission is attached to a high speed shaft which turns a generator
that makes electricity.
If the wind gets too high, the turbine has a brake that will keep the blades from turning and being damaged.
 And wind speeds must be above 12 to 14 miles per hour to turn the turbines
fast enough to generate electricity. The turbines usually produce about 50
to 300 kilowatts of electricity each. A kilowatt is 1,000 watts (kilo means
1,000). You can light ten 100 watt light bulbs with 1,000 watts. So, a 300
kilowatt (300,000 watts) wind turbine could light up 3,000 light bulbs that
use 100 watts.
And wind speeds must be above 12 to 14 miles per hour to turn the turbines
fast enough to generate electricity. The turbines usually produce about 50
to 300 kilowatts of electricity each. A kilowatt is 1,000 watts (kilo means
1,000). You can light ten 100 watt light bulbs with 1,000 watts. So, a 300
kilowatt (300,000 watts) wind turbine could light up 3,000 light bulbs that
use 100 watts.
Together these three places make enough electricity
to supply an entire city the size of San Francisco with power! About 30 percent
of the world's wind-generated electricity is found in California. Other countries
that use a lot of wind energy are Denmark and Germany.
BIOMASS ENERGY
Biomass is matter usually thought of as garbage. Some of it is just stuff
lying around -- dead trees, tree branches, yard clippings, housing rubble,
left-over crops, and bark and sawdust from lumber mills. It can even include
trash, paper products and other household waste you'd normally send to the
dump in your weekly trash pick up.
This stuff nobody seems to want can be used to produce electricity, heat, compost material or fuels. Composting material is decayed plant or food products mixed together in a compost pile and spread to help plants grow.
Using biomass does not add to global warming. Plants use and store carbon dioxide when they grow. This is then released when the plant material is burned. So using biomass closes this cycle of storing carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a gas that, when there's too much, can contribute to the "greenhouse effect" and global warming.
Biomass can be recycled and made into other products such as paper and fertilizer. Because biomass is reused and recycled, less garbage is sent to the dump. Less land is needed for "landfills" to hold the garbage.
And the use of biomass is environmentally friendly because the biomass is reduced, recycled and then reused. Today, many new ways of using are still being discovered. One way is to produce ethanol, an alcohol fuel for cars. Anotherway is to change biomass to combustible gases for electricity production.
The wood or biomass pellets you burn in a wood stove are other examples of using biomass to produce heat energy for your home.
Conclusion
To make sure we have plenty of energy in the future, it's up to all of us
to use energy wisely.
We must all conserve energy and use it efficiently. It also up to those of you who will want to create the new energy technologies of the future.
One of you might be another Albert Einstein and find a new source of energy. It's up to all of us. The future is ours but we need energy to get there.