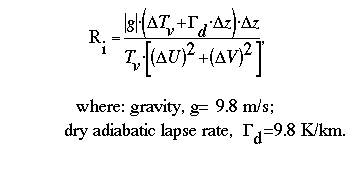Introduction : This calculator calculates the bulk Richardson number, Ri. This number determines whether the wind shear is strong enough to cause turbulence in statically stable air. The change in geopotential height usually determines the stability of the air. If the change in geopotential height is small, the flow is dynamically unstable and turbulent. This means that the bulk Richardson number is less than the critical Richardson number, Ric, where the critical Richardson number is equal to 0.25 (Ric>Ri). In this calculator, you have eight input values:
- Temperature at the highest geopotential height (T1)
- Temperature at the lower geopotential height (T2)
- Wind speed toward East at the highest geopotential height (U1)
- Wind speed toward East at the lower geopotential height (U2)
- Wind speed toward North at the highest geopotential height (V1)
- Wind speed toward North at the lower geopotential height (V2)
- Geopotential height at the highest geopotential height (z1)
- Geopotential height at the lower geopotential height (z2)
The algorithm for the whatever it is is:
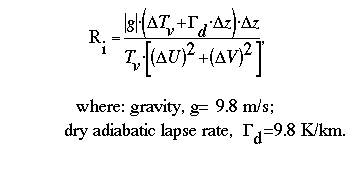
|
Richardson Calculator
|