|
|
Flow Obstructions and WakesAs mentioned earlier, thermal and mechanical turbulence can often occur together and enhance each other's influence. Imagine an isolated rectangular building with the background wind from the west (left). Although the wind flow around this obstruction is very complex, an idealized, general cross-section is shown below. Moreover, the direction changes from minute to minute, changing the part of the obstacle facing the wind and thus the associated turbulent eddies.
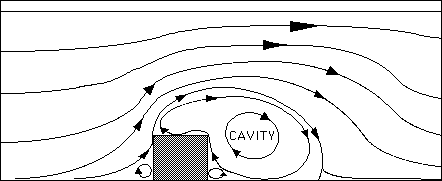 Notice first of all that a circular cavity of relatively slow moving air forms on the lee side (downwind side) of the building. The air in this cavity does not mix efficiently with other air; instead, it tends to circulate within the cavity and not leave the area. This cavity has the potential to acquire high concentrations of any substances introduced into the rotation because the air does not mix with outside air. Notice also two other smaller rotations that form near the base of the building on both the windward (upwind side) and lee sides. The flow that surrounds and is affected by the obstruction is known as the wake. The effect of the wake weakens with increasing distance from the obstruction. The height of the wake region often extends up to about 2.5 times the height of the building/obstruction, and extends downwind up to 10 times the height of the obstruction/building. When we look at the same building and flow in a 3-dimensional view, we notice more complex features.
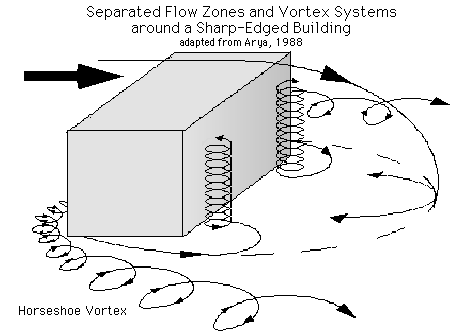 From this perspective, the wind pattern is much more intricate. To illustrate other flow patterns, the main cavity has been removed. Here, two features really stand out -- the two vertical vortices on the lee side of the obstruction and the horizontal vortex system (called the horseshoe vortex). If you were to add sufficient surface heating to the system, the situation would become even more complex, with eddies and vortices rising into the unstable atmosphere. Confused? Have a question? If so, check out the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) page or send mail to the OS411 tutor (os411tutor@shodor.org) with your question! Report technical/content problems here |
|
|