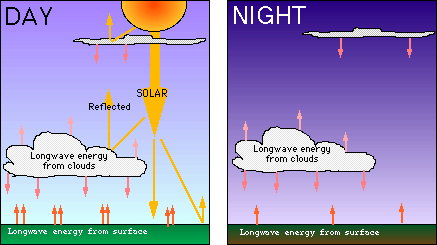
Cloud CoverClouds play an important part in energy balance. Clouds both reflect and release radiation efficiently. Shortwave radiation from the sun is efficiently reflected, and longwave radiation from the earth is efficiently absorbed and emitted. High, thin clouds radiate heat (longwave radiation) back towards the earth, whereas low, usually thicker clouds, reflect incoming sunlight, but also absorb and emit heat from the surface. That is why in the summer, very cloudy days seem cooler than clear days, and cloudy nights seem warmer than clear nights. The clouds act as trapping agents, keeping the surface heat in, but not allowing much more to enter or escape (see diagram below).
 Report technical/content problems here |
|
|