| |
Gas Pressure

Credit:
Gases exert pressure on the walls of a container. This is clear enough
from common experiences like blowing up a balloon or filling a tire with
air. On a macroscopic level, pressure
is defined as: the force exerted per unit of surface area or:
Pressure = force/area
Pressure is the result of gas particles colliding with surfaces. Imagine a strong hailstorm against a
window. The greater the number of collisions the greater the pressure so
that both gas concentration and the temperature of a gas will affect the pressure
observed at a surface. Just to give you some sense of what busy bees gas molecules are even
under normal conditions, consider a sample of nitrogen
gas confined to a room at 20o C and 1 atmosphere of pressure.
The most probable speed of the average particle in this gas sample is 1,100
mph. This speed changes as collisions with particles and walls of the container
occur. An average particle can only travel about 6.6 x 10-8
m before running into something and it undergoes about 7.7 x 109
collisions/sec.
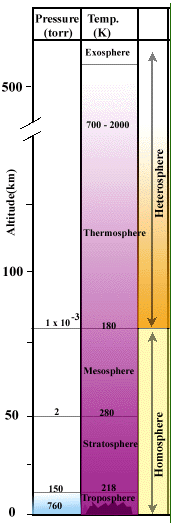 |
Due to gravitational attraction to the the Earth, the gases that form
the Earth's atmosphere are pulled towards its surface and exert a force
on everything near its surface. The force of all of these gases creates
the atmospheric pressure
of about 1 atm or 14.7 pounds per square inch that we are designed to live in. At higher altitudes where there is less atmosphere the atmospheric pressure is reduced. As you move further and further away from the surface of the earth the gas pressure is reduced even more as can be seen in the diagram
at left. Pressure is generally expressed in units of atmospheres (atm),
Torr, or mmHg,
Units of Pressure
| 1 pascal (Pa) |
1 N/m2 = 1 kg/m * s2 |
| 1 atmosphere (atm) |
1.01325 * 105 Pa |
| 1 atmoshphere (atm) |
760 torr = 760 mmHg |
| 1 bar |
105 Pa |
A good demonstration of the effects of gas pressure can be viewed in
the following movie. So-called "empty" containers are in fact, filled with gases.
As the movie shows,when most of those gases are removed, normal atmospheric pressure crushes the evacuated container. View Movie |
Report technical/Content problems here
|
|