|
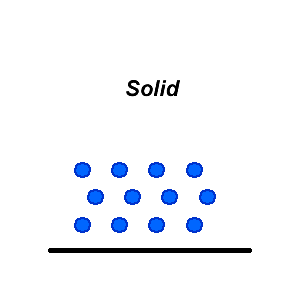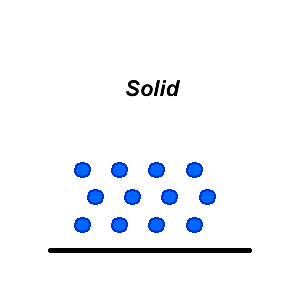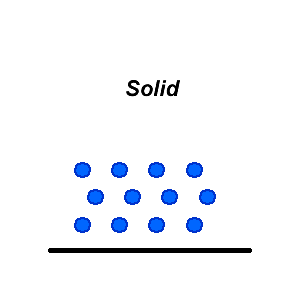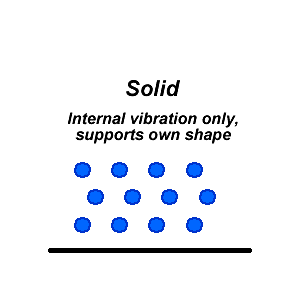
In solids, the forces of attraction between molecules are very strong. As a result, movement is restricted. Solids can have highly ordered structures like crystals, or disordered amorphous structures like glass. The shape of a solid is fixed by the strong bonds between all the atoms and cannot be changed by the shape of a container.
Most elements are solids at normal temperature and pressure. The noble gases are, of course, gaseous. There are 5 other elements that are generally encountered as gases -- O2, N2, F2, Cl2 and H2. Bromine isis a liquid at room temperature but boils to form the gas Br2 at even slightly elevated temperatures. Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at normal temperatures.
Ionic substances in their pure forms are always solid, however, many ionic substances dissolve easily in water forming a solution. In chemistry, matter that is originally in the solid, liquid or gaseous phase that is dissolved in water is said to be in the aqueous phase. In chemical equations this is shown by the abbreviation "aq". Purists may quibble with the treatment of the aqueous phase as a separate state of matter. At the molecular level, the dissolved substance fits in the position that would have been occupied by a molecule of the solvent if it were pure solvent. In order for a substance to dissolve in a solvent, the size and physical characteristics of the dissolving material must be very similar to those properties in the solvent. That is ... like dissolves like.
|
|