| |
Periodic Trends
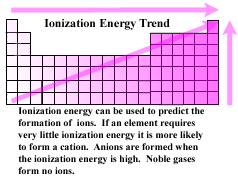
| Pulling an electron away from a nucleus to form a cation requires energy
. The powerful attraction between the oppositie charges of the electron
and the nucleus of the atom must be overcome. Ionization energy is the energy required to completely remove one mole
of electrons from one mole of gaseous atoms or ions. Ions with low
ionization energies tend to form cations. With the exception of noble
gases, ( that almost never form ions), elements that have very high ionization
energies tend to form anions. The general trend in ionization energies
can be mapped on a periodic table. |
 |
|
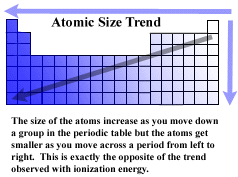
The regularity seen in properties of elements arranged in the periodic
table is at least in part, due to the addition of protons to the atom moving
from left to right across a period. Going from top to bottom of any group
or column in the periodic table the atomic radius of the the atoms increases.
This makes sense since there wiill also be more electrons added to the
atom. The larger the number of electrons in any group, the larger
the size of the atom.
. |
But the opposite trend is seen when move from left to right across a period.
This latter tendency is more difficult to explain. The new electrons
being added as you move right in a period are being added to the same shell
of the atom (remember the idea of the electrons moving around the nucleus
of the atom inside a prescribed spherical volume like the volumes defined
by the layers of an onion) so they don't get much distance from the
nucleus. At the same time, the nucleus is itself getting a stronger
and stronger positive charge from the addition more and more protons. Because
of this increasing nuclear charge, even though there are more and more
electrons being added, the radius of the atoms, as you move from left to
right across the periodic table, the electrons are drawn in tighter and
tighter and the radius of the atom becomes smaller.
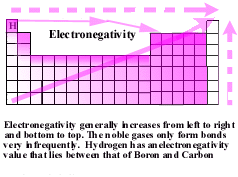
| Chemical bonds between two or more atoms can result
from the equal sharing of one or more electrons. However, some atoms have a greater
ability to attract electrons in a bond. These atoms are said to be
electronegativity.
The most electronegative atoms are in the upper right hand corner
of the periodic table, F, and Cl. Consider a bond between a carbon atom and a chlorine atom. Because of their greater ability
to attract electrons than say, a carbon atom, the electrons from the carbon atom bonded to a chlorine atom
are not shared equally. The electron density is greatest near
the most electronegative atom, in this case the chlorine atom. This creates a nonsymetric electron
cloud with a slight negative charge near the more electronegative atom
and a slight positive charge near the more electropositive end of the bond. |
 |
Report technical/Content problems here
|
|